World Health Organization calls for mpox vaccine production surge as virus spreads
Geneva, Switzerland - The World Health Organization on Friday urged manufacturers to ramp up production of mpox vaccines to rein in the growing spread of a new, more dangerous strain of the virus.
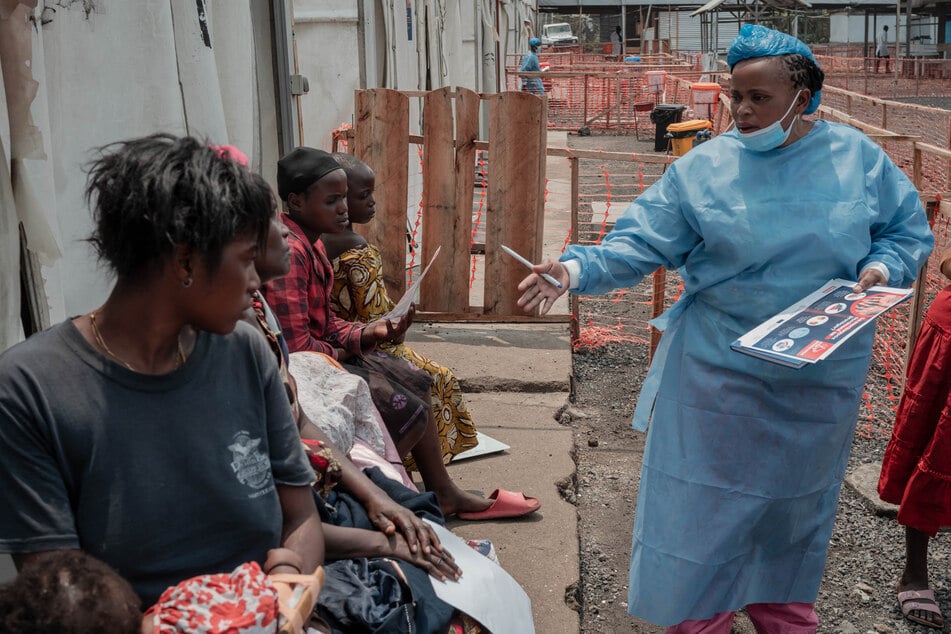

The WHO on Wednesday declared the surge in mpox a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) – its highest alert level – with cases soaring in the Democratic Republic of Congo and spreading beyond its borders.
"We do need the manufacturers to really scale up so that we've got access to many, many more vaccines," WHO spokeswoman Margaret Harris told reporters.
The WHO is asking countries with mpox vaccine stockpiles to donate them to countries with ongoing outbreaks.
Harris said mpox was "particularly dangerous for those with a weak immune system, so people who maybe have HIV or are malnourished," and was also dangerous for small children.
The WHO was due to issue recommendations following a first extraordinary meeting Thursday of the Standing Committee on Health Emergency Prevention, Preparedness and Response over mpox.
There are two subtypes of the virus: the more virulent and deadlier Clade 1, endemic in the Congo Basin in central Africa; and Clade 2, endemic in West Africa.
The upsurge in the DR Congo is being driven by separate outbreaks of two different Clade 1 strains of the virus, according to the WHO.
Mpox outbreak is a "complex picture" for health officials
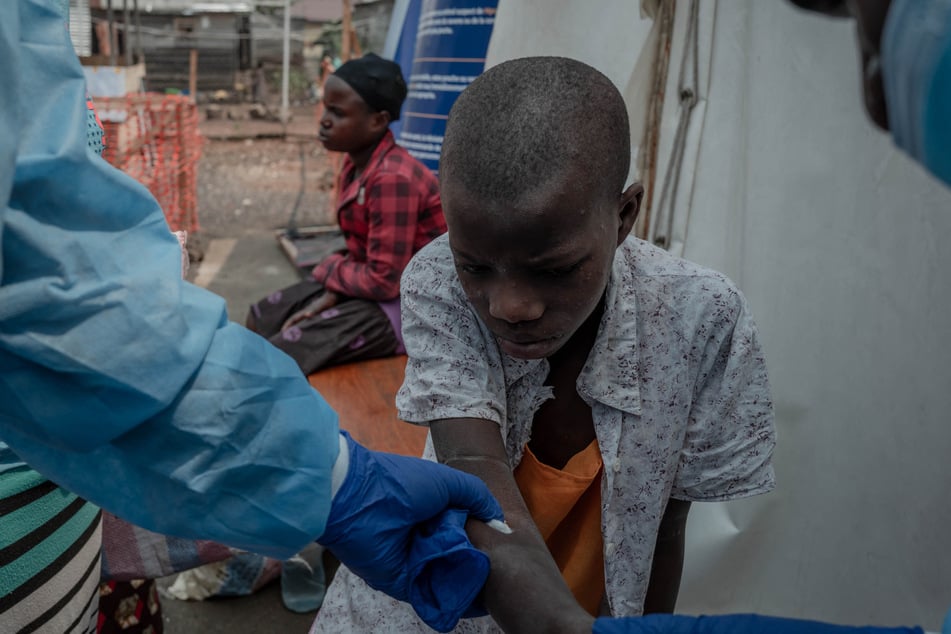
The first is an outbreak in northwestern DRC of what was previously known as Clade 1, now called Clade 1a, which is endemic in that part of the country. This outbreak is primarily affecting children and is spread through multiple modes of transmission.
The second is an outbreak in northeastern DRC of a new offshoot of Clade 1 called Clade 1b, which was first detected in September last year and is spreading rapidly, mainly through sexual transmission among adults.
The rapid spread of the new Clade 1b offshoot and its detection in neighboring countries were the main reasons behind the WHO's decision to declare a PHEIC.
That said, Clade 1a cases have also been reported this year in the Central African Republic and Congo-Brazzaville, while Clade 2 has been reported in Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Nigeria, and South Africa, WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus told the standing committee.
"It's a complex picture, and responding to each of these outbreaks and bringing them under control will require a complex, comprehensive, and coordinated international response," he said.
Cover photo: GUERCHOM NDEBO / AFP

