How "virus hunters" are tracking threats to head off the next pandemic before it starts
A global network of doctors and laboratories is working to pinpoint emerging viral threats, including many driven by climate change, in a bid to head off the world's next pandemic.
The coalition of self-described "virus hunters" has uncovered everything from an unusual tick-borne disease in Thailand to a surprise outbreak in Colombia of an infection spread by midges.
"The roster of things that we have to worry about, as we saw with COVID-19, is not static," said Gavin Cloherty, an infectious disease expert who heads the Abbott Pandemic Defense Coalition.
"We have to be very vigilant about how the bad guys that we know about are changing... But also if there's new kids on the block," he said.
The coalition brings together doctors and scientists at universities and health institutions across the world, with funding from healthcare and medical devices giant Abbott.
By uncovering new threats, the coalition gives Abbott a potential headstart in designing the kinds of testing kits that were central to the COVID-19 response.
And its involvement gives the coalition deep pockets and the ability to detect and sequence but also respond to new viruses.
"When we find something, we're able to very quickly make diagnostic tests at industry level," Cloherty said.
"The idea is to ringfence an outbreak so that we would be able to hopefully prevent a pandemic."
The coalition has sequenced approximately 13,000 samples since it began operating in 2021.
In Colombia, it found an outbreak of Oropouche, a virus spread by midges and mosquitoes, that had rarely been seen there before.
Phylogenetic work to trace the strain's family tree revealed it came from Peru or Ecuador, rather than Brazil, another hotspot.
"You can see where things are moving from. It's important from a public health perspective," said Cloherty.
Scientists discover the interplay between climate change and viral evolution
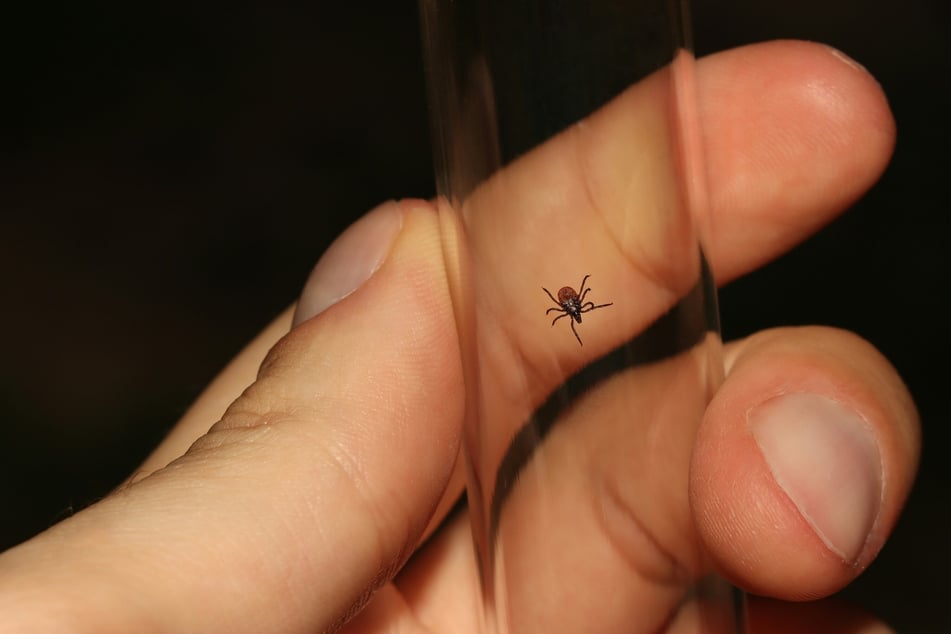

More recently, the coalition worked with doctors in Thailand to reveal that a tick-borne virus was behind a mysterious cluster of patient cases.
"At the time, we didn't know what virus caused this syndrome," explained Pakpoom Phoompoung, associate professor of infectious disease at Siriraj Hospital.
Testing and sequencing of samples that dated back as far as 2014 found many were positive for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTSV).
"Less than 10 patients had [previously] been diagnosed with SFTSV in Thailand... we don't have PCR diagnosis, we don't have serology for this viral infection diagnosis," Pakpoom said.
There is a growing need to track these threats as climate change expands the range of infectious diseases globally as the link between climate change and infectious disease is well-established and multi-faceted.
Warmer conditions allow vectors like mosquitoes to live in new locations, more rain creates more breeding pools, and extreme weather forces people into the open where they are more vulnerable to bites.
Human impact on the planet is also driving the spread and evolution of infectious disease in other ways: biodiversity loss forces viruses to evolve into new hosts and can push animals into closer contact with humans.
Phylogenetic analysis of the SFTSV strain in Thailand gives a snapshot of the complex interplay. It showed the virus had evolved from one tick with a smaller geographic range into the hardier Asian long-horned tick.
The analysis suggested its evolution was driven largely by pesticide use that reduced the numbers of the original tick host. Once the virus evolved, it could spread further in part because Asian long-horned ticks can live on birds, which are traveling further and faster because of changing climate conditions.
Climate change's fingerprints are in everything from record outbreaks of dengue in Latin America and the Caribbean to the spread of West Nile Virus in the United States.
While the coalition grew from work that preceded the pandemic, the global spread of COVID-19 offered a potent reminder of the risks of infectious disease.
"You have to be vigilant," Cloherty said. "Something that happens in Bangkok could be happening in Boston tomorrow."
Cover photo: SEBASTIEN BOZON / AFP