Ketanji Brown Jackson is confirmed to Supreme Court by the Senate
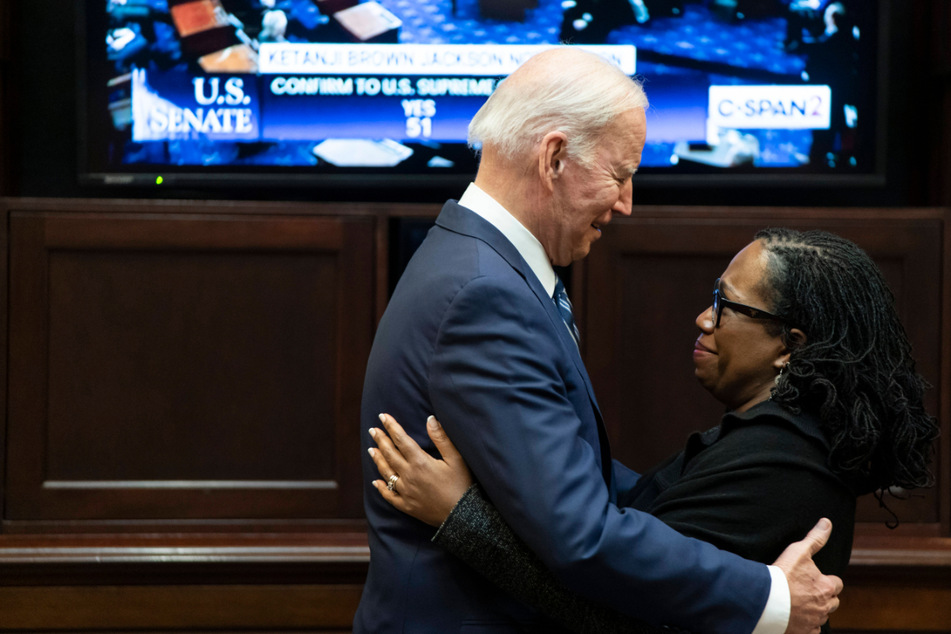
Washington DC – On Thursday, the Senate confirmed Judge Ketanji Brown Jackson to the Supreme Court, promoting the appellate judge to a lifetime seat no Black woman has ever occupied.
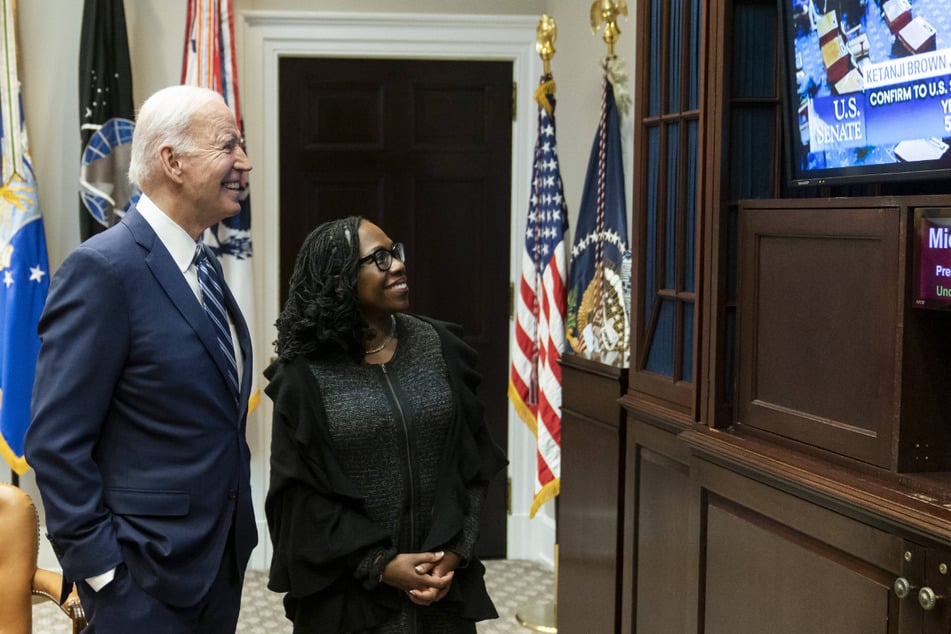

Jackson becomes only the sixth woman and third Black justice to ascend to the high court, which will for the first time have two Black members, three members of color, and four women.
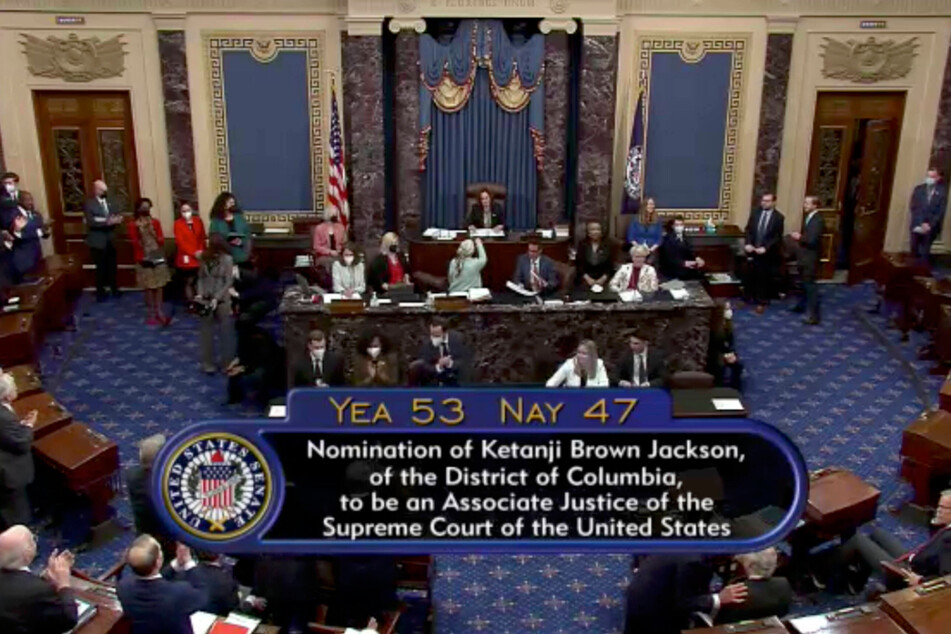
The 51-year-old shattered the proverbial glass ceiling with the Senate's 53-47 confirmation vote. Three Republicans — Sens. Susan Collins of Maine, Lisa Murkowski of Alaska, and Mitt Romney of Utah — joined every Democrat in supporting President Joe Biden's historic nominee.
Sen. Cory Booker, D-NJ, presided over the Senate as it passed a key hurdle Thursday afternoon, and Vice President Kamala Harris presided over the chamber during the final vote.
Biden’s first appointment to the Supreme Court won’t alter the ideological balance of a bench that now has a 6-3 conservative majority. But in appointing the first Black female justice, Biden hopes to energize Democrats heading into the midterm election and strengthen the court’s liberal minority with a new member who could serve for decades.
Jackson won’t be formally sworn in until this summer. Retiring Justice Stephen G. Breyer said he will step down at the end of the court’s current term, which will come at the end of June or early July, when decisions in all the pending cases have been issued. Those include some potentially far-reaching rulings on abortion, guns, religion, and climate change that Jackson will not take part in.
That gives Jackson, who once served as a law clerk for the justice she is replacing, the summer to prepare for the new term in October, which will include cases on the future of affirmative action and the Voting Rights Act.
Justices will hear arguments concerning the use of race as an admissions factor at Harvard and the University of North Carolina. Jackson, a Harvard alum, said she will not take part in the Harvard case because she has been a member of the university’s board of overseers since 2016. But the court could hear the UNC case separately, so she could participate in the decision.
Jackson will also be seated in time to hear Alabama’s challenge to a provision of the Voting Rights Act.
"An American giant upon whose shoulders others will stand tall"

Jackson’s impact on the court figures to be limited at the start. She will be the junior justice and one of only three Democratic appointees on a court whose agenda is set by the six conservatives, all Republican appointees.
But progressives point to her experience as a public defender and a federal trial judge, and say she could influence the court’s internal debates on matters of crime and punishment. They also say she could have a powerful voice on civil rights, not just within the court, but in dissent.
Since the retirement of Justice Thurgood Marshall in 1991, the high court has not had a Black justice who was an outspoken champion of civil rights and racial justice.
In his opening floor remarks Thursday morning, Senate Majority Leader Charles E. Schumer, D-N.Y., said it was "a joyous, momentous, groundbreaking day," though he also insisted America should’ve reached this milestone generations ago.
"America today is taking a giant step towards making our union more perfect," Schumer said. "People sometimes talk about standing on the shoulder of giants. Well, Judge Jackson will go down in history as an American giant upon whose shoulders others will stand tall, and our democracy will be better off for it."
The final Senate vote capped a 10-week process that began in late January with reports of Breyer’s retirement. To reach confirmation with a 50-50 Senate left little margin for error. Democrats had to use a tool that hadn’t been used to advance a Supreme Court nominee since 1853. After the Senate Judiciary Committee deadlocked on recommending Jackson on Monday, the full Senate narrowly voted to advance her nomination to the floor via a so-called discharge motion.
Breyer’s official retirement set in motion the search for an eminently qualified Black woman who could win Republican support. As a presidential candidate in 2020, Biden had pledged to nominate a Black woman to the high court. And as president, he gave himself an end-of-February deadline, assuring he would announce his decision during Black History Month.
In tapping Jackson, he chose a Harvard Law-educated judge who had been Senate-confirmed with bipartisan support on three previous occasions, including last June. Senate Democrats routinely touted her deep experience as a US District Court judge for the District of Columbia and then on the US Court of Appeals for the DC Circuit.
Jackson was endorsed by a wide array of groups and figures, most notably the Fraternal Order of Police, the International Association of Chiefs of Police and retired federal judges J. Michael Luttig and Thomas B. Griffith. Democrats highlighted the backing of police unions — and Jackson’s family’s law enforcement service — to rebut GOP claims that Jackson was soft on crime.
Cover photo: IMAGO/ZUMA Wire

